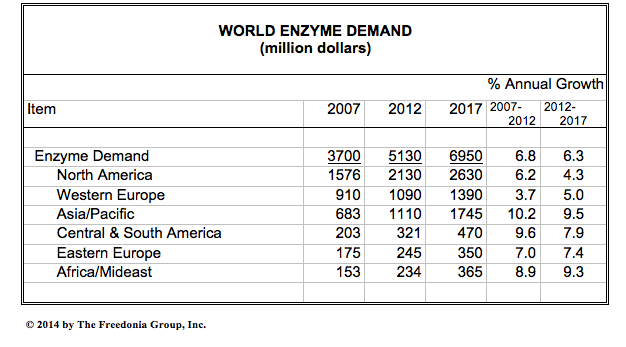
World enzyme demand is forecast to increase 6.3 percent per year to nearly $7 billion in 2017, according to data included in a new report, World Enzymes. Enzymes are frequently used in the manufacturing of cleaning products.
Demand will be driven by rising per capita incomes in developing countries, which will result in strong gains in enzymes associated with the production of consumer goods, including food and beverages, cleaning products, and animal feed. In specialty markets, demand will benefit from falling costs of DNA sequencing, which will allow for rising use of enzymes in research and biotechnology and diagnostic applications.
Enzyme demand will face challenges in the large North American biofuel market as rising opposition to grain-based biofuels and delays in the commercialization of next generation cellulosic biofuel technologies limit advances. These and other trends are presented in World Enzymes, a new study from The Freedonia Group, Inc., a Cleveland-based industry market research firm.
According to Freedonia analyst Jason Carnovale, “The rapidly growing middle class populations of countries such as China and India will be a key driver of growth through the forecast period.”
Rising per capita incomes will support consumer demand for higher value goods, such as detergents and food products. Consumption of Western style diets, which are associated with demand for meat, baked goods, and dairy products, will continue to rise among emerging middle class populations. In turn, these foods will be increasingly produced through the use of enzymes, both in animal feed and in food processing applications. Compounding these positive effects will be strong overall economic and industrial growth, which will benefit a number of industrial enzyme markets. Similar trends in Central and South America, Eastern Europe, Africa, and the Middle East will lead to above average gains in these regions as well.
In developed countries, economic and industrial growth will tend to be slower, resulting in more modest expansion of enzyme use. Additionally, the markets in North America, Western Europe, and Japan tend to be more mature, further limiting growth prospects. However, niche opportunities will arise, supported by the positive environmental profile enzymes offer. Enzymes which can substitute for non-renewable chemicals, reduce energy consumption, or decrease the production of harmful wastes will see the best opportunities. In the longer term, enzymes are expected to play a key role in the emergence of the renewable chemicals industry, which currently remains nascent.
 The Down and Dirty on Cleaning in Virus Season
The Down and Dirty on Cleaning in Virus Season How Surfactant Use is Expanding in Commercial Cleaning
How Surfactant Use is Expanding in Commercial Cleaning Operational Excellence Series 2025: Better Budgeting
Operational Excellence Series 2025: Better Budgeting